Gender Differences in Response to East Asian Erotic Stimuli: A Validated Image Dataset
Summary
- This project developed and validated a culturally sensitive erotic image dataset for East Asian populations, filling a gap in non-Western representation in sexual stimuli research.
- The dataset includes 237 erotic and 108 control images, categorized by gender and degree of nudity, with self-reported ratings of sexual arousal, pleasantness, and attractiveness from heterosexual male and female participants (n = 40).
- Key findings: Males rated nude female images highest, whereas females rated semi-nude male images highest, showing gender-specific patterns in sexual arousal and perception.
Challenge
-
Identifying relevant users: There was a limited availability of datasets featuring East Asian participants, which constrained research on motivation and human sexuality within the East Asian—particularly Chinese—population.
-
Recruitment challenges: It was necessary to include all stimulus categories—control, semi-nude, and nude images—while ensuring that all depicted non-celebrity individuals to prevent confounds related to familiarity or attraction bias.
Solutions to the challenge
- Curated a balanced dataset of 237 erotic and 108 control images, evenly distributed across six categories of male and female imagery.
- Controlling for familiarity effects: Selected non-celebrity models and standardized image quality to reduce recognition and preference biases.
- Collected anonymous ratings from both females and males on arousal, pleasantness, and attractiveness to capture nuanced responses.
- Conducted statistical validation by analyzing gender differences across stimulus categories.
Goal
To build a validated erotic image dataset for East Asian sexuality research, identify nuanced gender differences among Chinese participants, and contribute to cross-cultural comparisons in emotional and sexual processing studies.
Why it matters
- Fills a critical gap in cross-cultural psychological research by including East Asian perspectives.
- Supports sexology, neuroscience, and affective science with culturally relevant stimuli.
Research Process
Stage 1: Identifying the problem
- Reviewed prior work showing that most erotic image databases (e.g., IAPS, NAPS) are Western-centric.
- Recognized that East Asian cultural norms toward sexuality and nudity differ substantially, leading to potential cultural mismatch in experimental stimuli.
- Defined the goal to construct and validate a new dataset reflecting East Asian preferences.
Stage 2: Stimulus Development & Participant Recruitment
- Developed 345 digital photographs of East Asian adults across six levels of sexual explicitness (dressed to nude).
- Curated stimuli from non-royalty and permissive-use sources, removing logos, piercings, and strong facial expressions for consistency.
- Recruited 40 heterosexual Chinese college students (20 males, 20 females; M = 22.35 years) screened via the Kinsey Scale.
- Controlled for emotional factors using BDI and SAS assessments; no gender differences were observed.
- Obtained informed consent and IRB approval, ensuring ethical standards and cultural relevance.
Stage 3: Data Collection & Rating
- Participants viewed opposite-sex images and rated them for:
- Sexual arousal
- Pleasantness
- Sexual attractiveness
- Randomized presentation order and timing to ensure consistent exposure.
Stage 4: Data Analysis
- For female participants, conducted one-way ANOVAs to compare ratings of sexual arousal, pleasantness, and sexual attractiveness across dressed, semi-nude, and nude male images.
- For male participants, due to a violation of homogeneity of variance, applied Welch’s heteroscedastic F tests followed by Games–Howell post-hoc analyses to assess differences in responses to female images.
Results
-
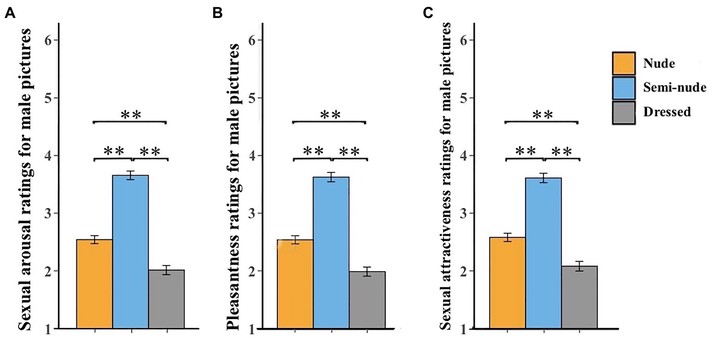
Females’ ratings of male pictures:
- Sexual arousal, pleasantness, and attractiveness were highest for semi-nude males, followed by nude males, and lowest for dressed males.
- Indicates that females preferred moderately revealing stimuli rather than fully nude images.
-
Males’ ratings of female pictures:
- Sexual arousal, pleasantness, and attractiveness were highest for nude females, followed by semi-nude females, and lowest for dressed females.
- Shows that males preferred fully nude stimuli, consistent across all rating dimensions.
-
Gender differences:
- Females preferred semi-nude males, whereas males preferred nude females, highlighting distinct sexual preferences and cultural influences.
- Differences may reflect cultural conservatism among Chinese females and evolutionary mating strategies.
-
Dataset utility:
- Enables selection of stimuli based on participant sex and normative ratings, supporting research in sexual reward, perceptual gaps, and clinical sexual dysfunction studies.
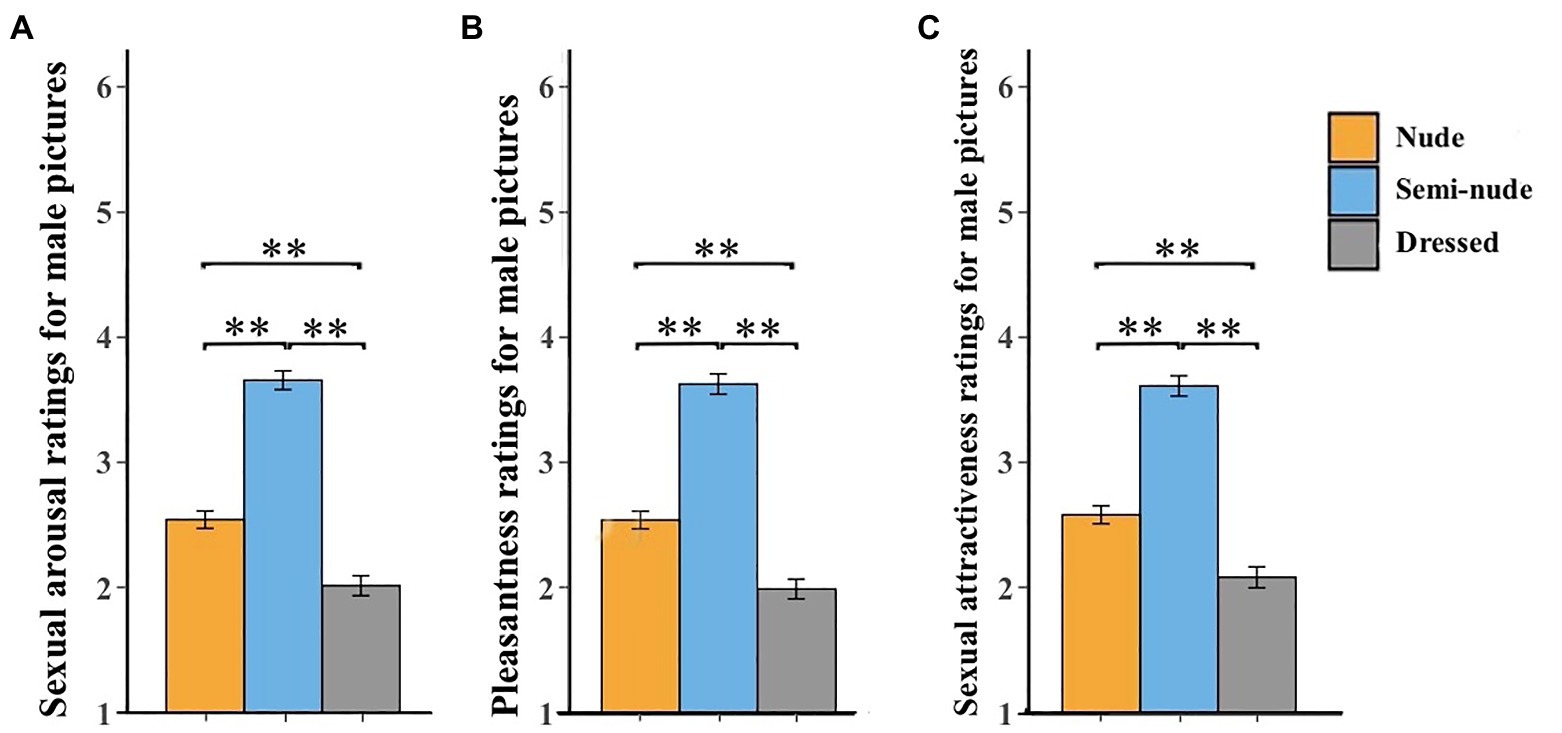
Females’ ratings of sexual arousal (A), pleasantness (B), and sexual attractiveness (C) for male pictures.
Error bars represent standard errors of the mean. p < 0.01.
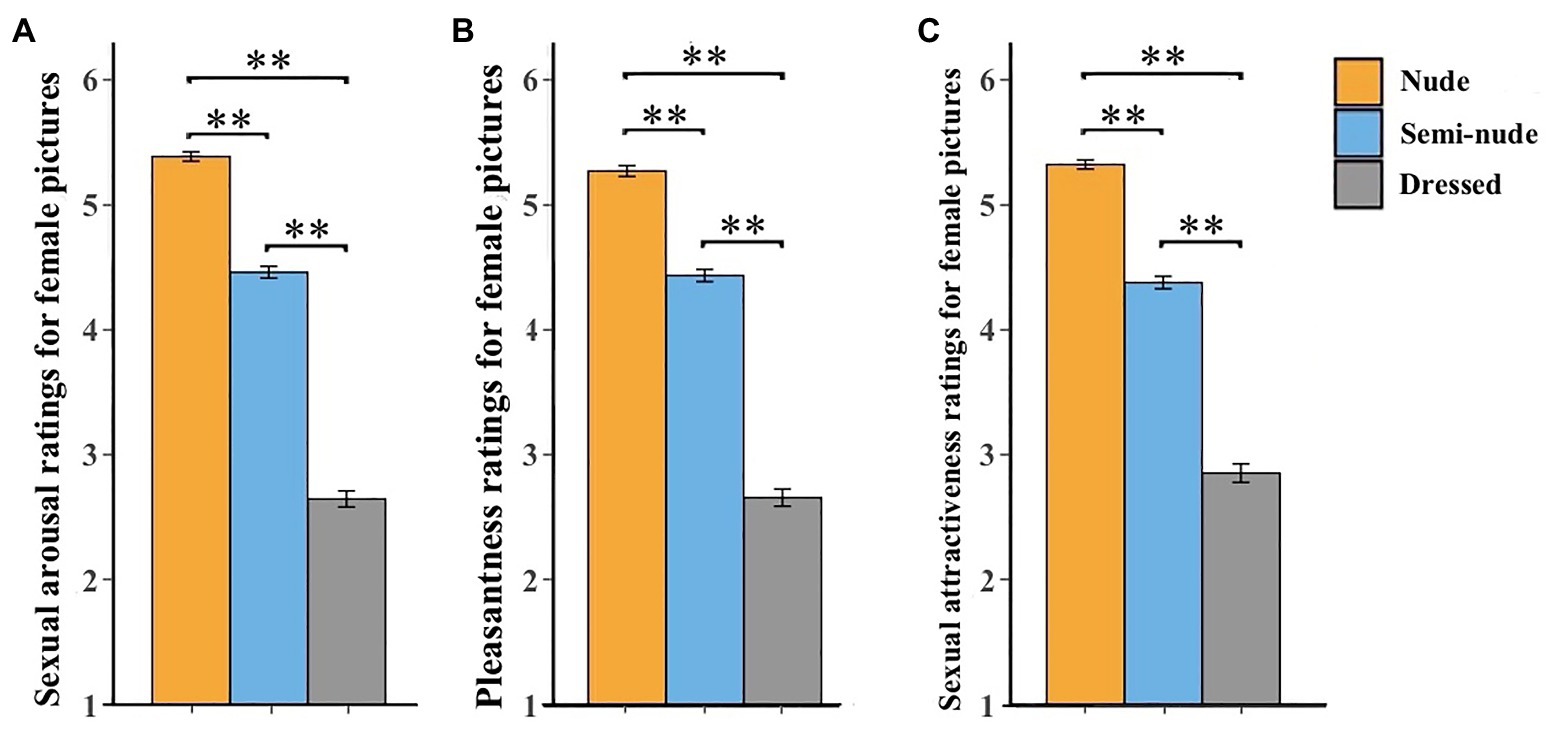
Males’ ratings of sexual arousal (A), pleasantness (B), and sexual attractiveness (C) for female pictures. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean. **p < 0.01.p < 0.01.
Reflection
This research produced one of the first validated East Asian erotic image databases, providing a critical resource for cross-cultural and affective studies.
It highlights how gender and culture jointly shape erotic perception, underscoring the need for diverse, culturally attuned research tools.
Future directions include expanding the dataset to include sexual minority participants and exploring neurophysiological correlates of arousal across cultural contexts.
Programming & Tools Summary
| Stage | Programming Language/Software | Key Libraries / Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | E-Prime, Qualtrics | |
| Data Cleaning | Python | Pandas, NumPy, regex |
| Statistical Analysis | R | |
| Visualization | R | ggplot2 |